Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction – Why Gabions Matter Today
From ancient fortifications to modern landscaping masterpieces, gabions have stood the test of time. These wire mesh containers filled with rock or other materials are now widely used in retaining walls, erosion control, and even outdoor furniture. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about gabions—what they are, how they work, their applications, and why they’re a smart, sustainable choice.
What is a Gabion?
A gabion is a cage, cylinder, or box made from welded or woven wire mesh, filled with stones, concrete, or even recycled materials. Originally used in military defense, gabions are now a key solution in civil engineering and landscape architecture due to their strength, versatility, and eco-friendliness.
The Origin and Evolution of Gabions
The term “gabion” derives from the Italian word gabbione, meaning “big cage.” The concept dates back to ancient Egypt and the Roman Empire, where soldiers filled baskets with stones to build fortresses. In the 20th century, gabions evolved into engineered solutions for soil stabilization, river control, and infrastructure reinforcement.
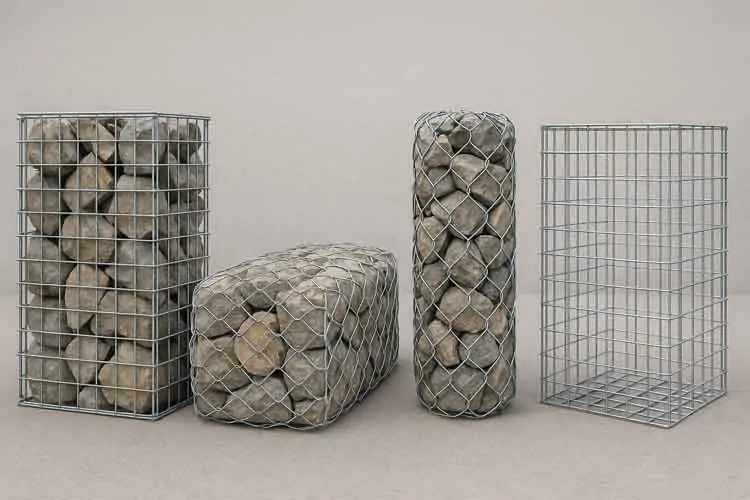
Types of Gabions
Depending on the project, gabions come in various shapes and mesh configurations:
-
Gabion Baskets (Boxes): Rectangular units used in retaining walls.
-
Gabion Mattresses: Shallow versions for riverbed and erosion control.
-
Gabion Cylinders/Sacks: Ideal for underwater or temporary structures.
-
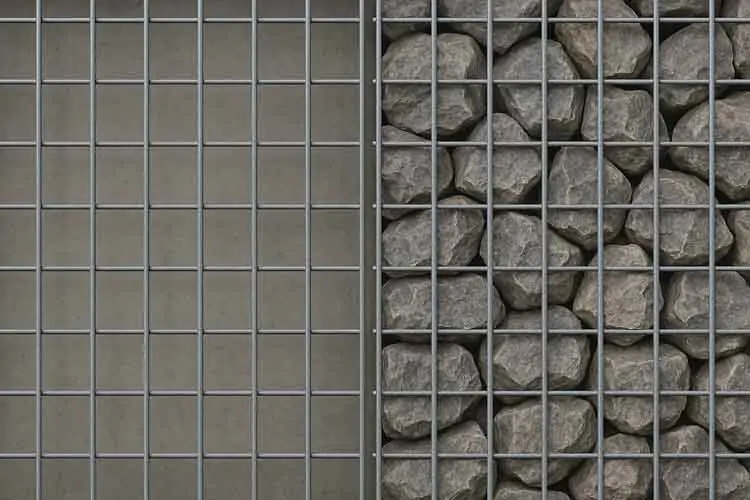
Welded Mesh Gabions: Pre-assembled and rigid, ideal for architectural uses.
-
Woven Wire Gabions: Flexible, great for uneven terrains.
What is the Purpose of a Gabion?
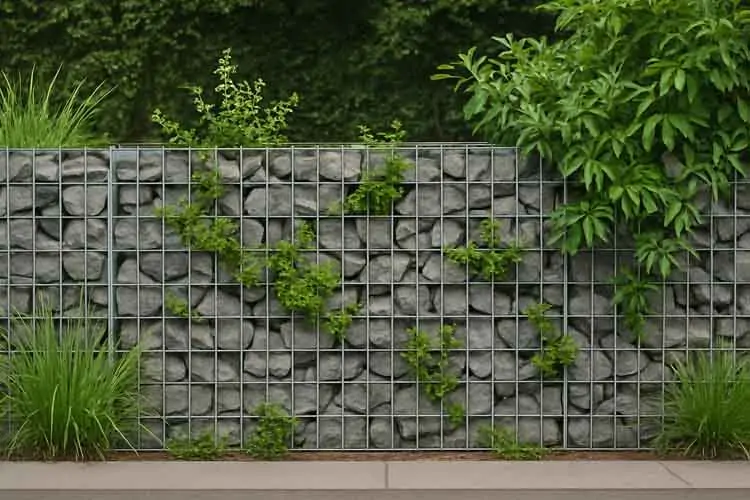
Gabions serve both structural and aesthetic functions. They stabilize slopes, prevent erosion, support retaining walls, and absorb energy from flowing water. In landscaping, they offer texture, contrast, and functionality—often doubling as furniture or decorative features.
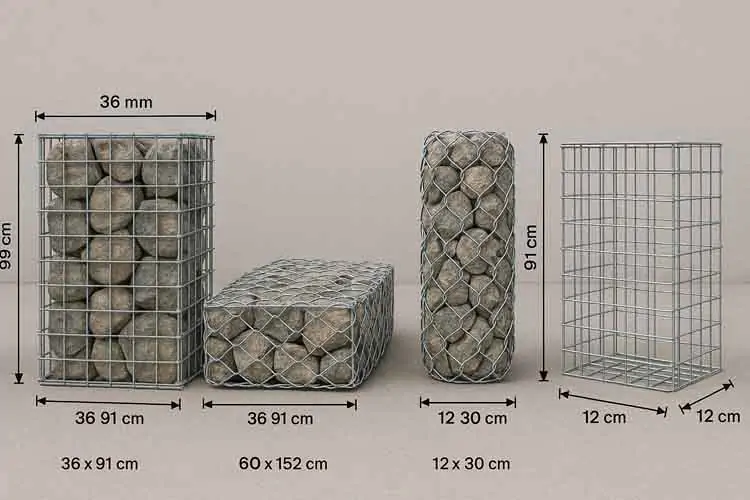
Standard vs Custom Sizes
Gabions are available in standard sizes such as 2m x 1m x 1m or 1m x 1m x 0.5m. However, many manufacturers offer custom sizes to meet specific project requirements, whether it’s a curved wall or a compact planter box.
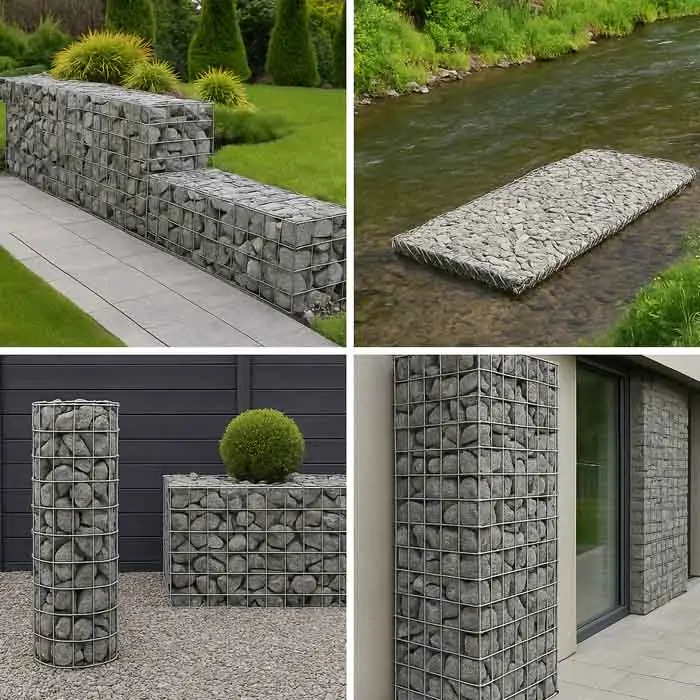
Common Applications of Gabions
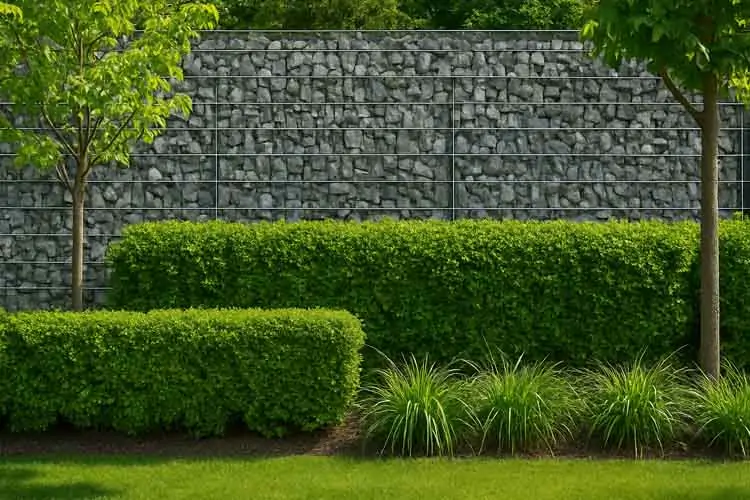
Gabion Wall
Used in roadways, properties, and commercial buildings, gabion walls offer a natural look and solid structure.
River Erosion Control
Gabions are placed along riverbanks to reduce flow velocity and prevent soil loss.
Garden Retaining Wall
Smaller baskets filled with local stones can create beautiful, eco-friendly terraces.
Outdoor BBQ and Tables
Gabions make sturdy bases for grills, countertops, or dining tables.
Outdoor Benches and Seating
Combine wood planks and gabions for rustic, weatherproof seating areas.
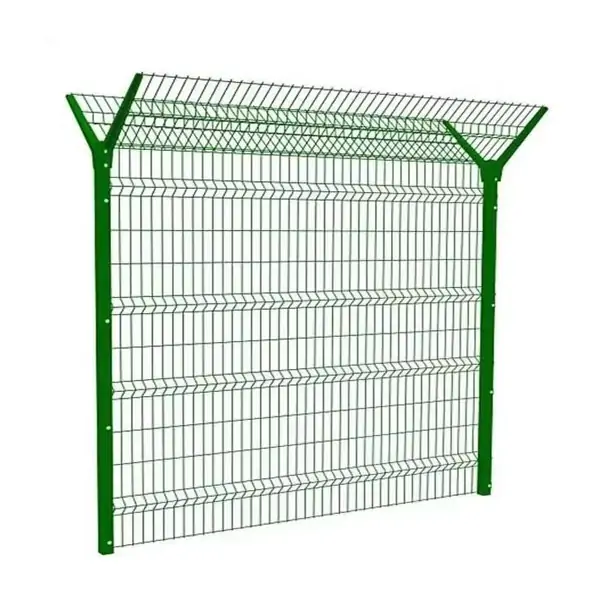
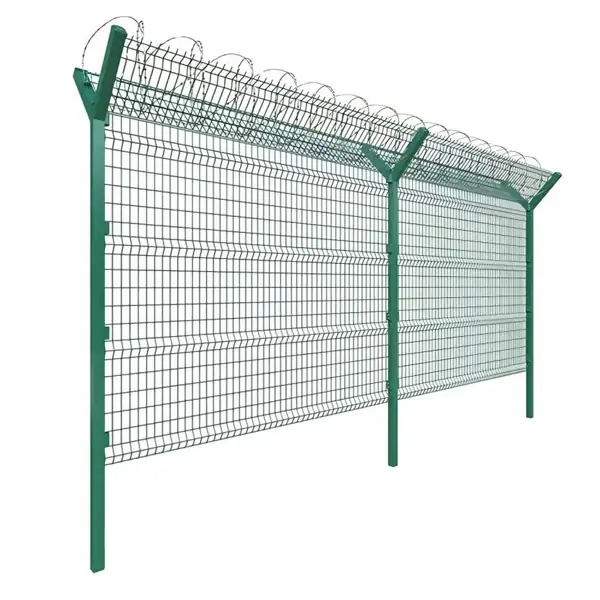
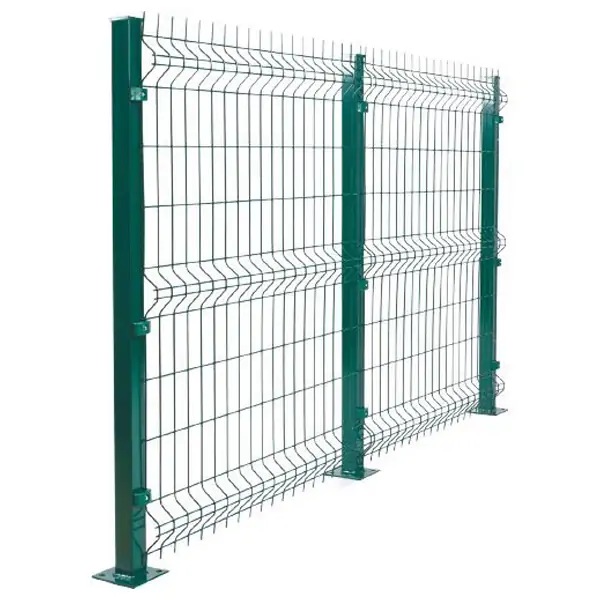
Fences and Freestanding Walls
Stacked gabions can form secure property boundaries or noise barriers.
Water Features
Use gabions as a frame for cascading waterfalls or bubbling fountains.
Planters
Gabions double as garden beds, providing drainage and structure.
Benefits of Gabions
Cost-Effective
Gabions often use locally sourced fill materials, lowering transportation and production costs.
Long-Lasting
With proper coating (galvanized or PVC), gabions can last over 50 years, even in harsh environments.
Simple to Install
No need for heavy machinery or concrete—just assemble, place, and fill.
Eco-Friendly
Gabions encourage plant growth, allow water permeability, and blend naturally into surroundings.
Customizable Design – A Personal Touch
Gabions can be curved, stacked, or layered creatively. They accommodate a wide range of design styles.
Efficient Assembly and Quality Materials
Pre-fabricated welded baskets and spiral binders allow fast, secure installation.
Product Variety
Manufacturers offer gabions in different mesh sizes, coatings, and configurations, suited for both functional and decorative projects.
How to Install a Gabion – Step by Step
-
Site Preparation: Level the ground, install foundation if needed.
-
Assemble Gabion Baskets: Connect panels with spirals, hog rings, or clips.
-
Position and Anchor: Place baskets, ensure alignment, anchor if needed.
-
Filling: Use clean, hard stone or concrete rubble.
-
Layer and Compact: Fill in layers, interlock rocks manually.
-
Close and Secure Lids: Tie down lids with wire or spirals.
How to Get Started with Your Gabion Project
-
Choose Your Type: Basket, wall, planter, or furniture?
-
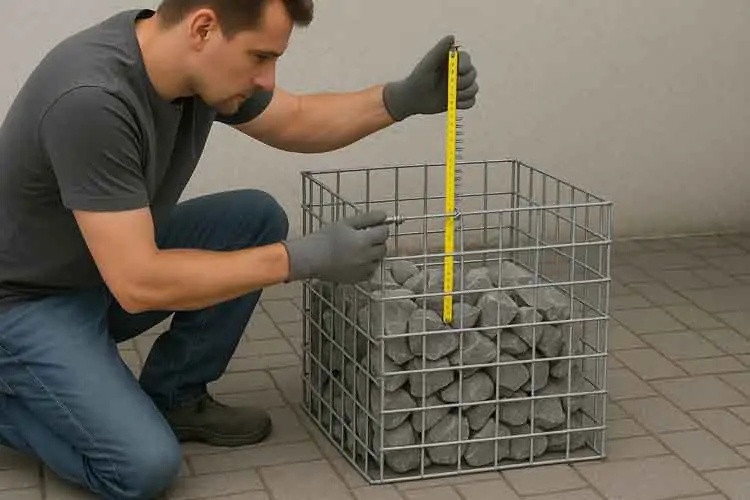
Measure Your Space: Get exact dimensions.
-
Select Materials: Mesh type, rock fill, coating.
-
Consult Supplier: For design support or custom orders.
-
DIY or Hire a Pro: Smaller projects can be done by yourself.
Conclusion
Gabions are more than just wire cages filled with stone—they’re a powerful blend of engineering strength and natural beauty. Whether you’re building a riverbank wall, a backyard BBQ table, or a commercial retaining system, gabions offer a durable, affordable, and eco-friendly solution.
So, are you ready to build your own gabion masterpiece? Let’s get started.