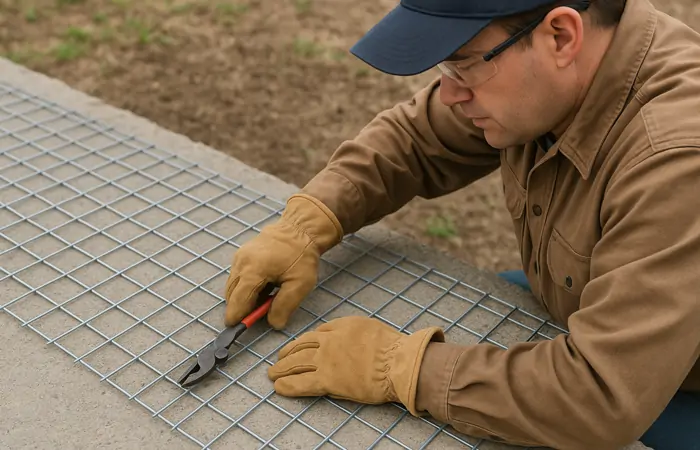
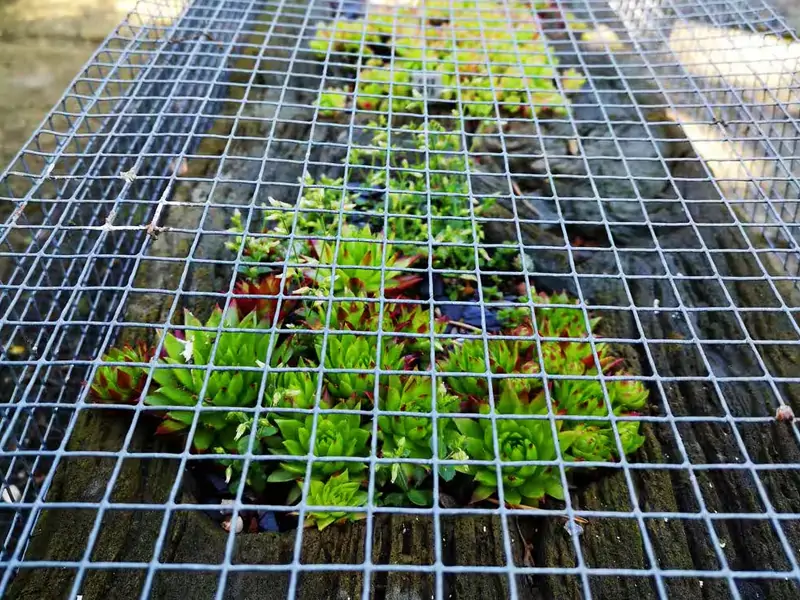
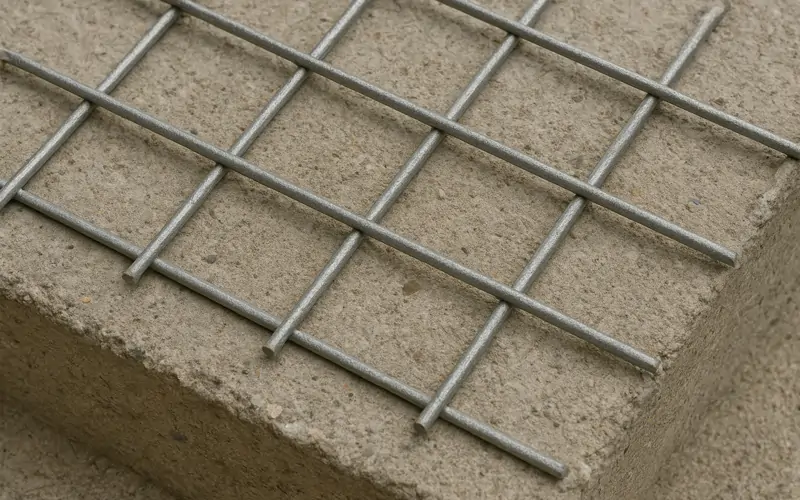
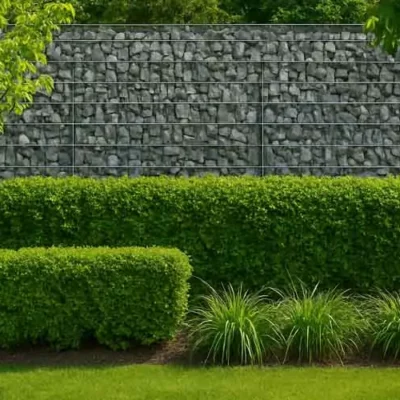
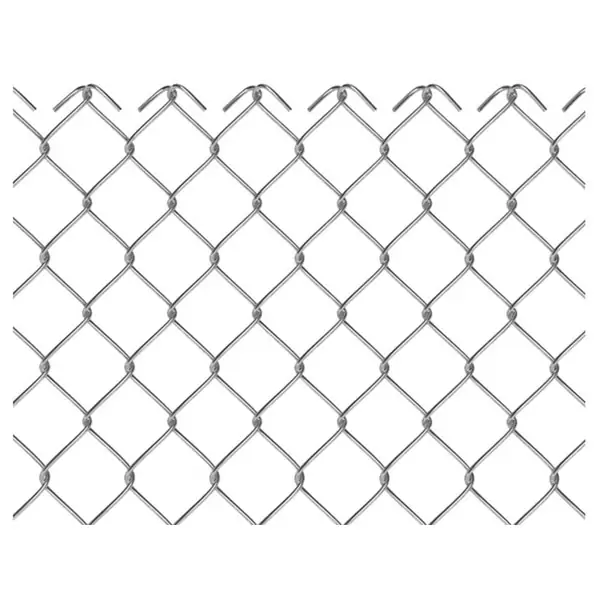
Hardware cloth might not be the most glamorous building material, but it is undoubtedly one of the most versatile. Whether you’re constructing a chicken coop, reinforcing concrete, or building a custom garden enclosure, hardware cloth is a go-to solution. It’s durable, corrosion-resistant, and adaptable to both residential and industrial needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about hardware cloth—from the different types and materials available, to its many applications, fabrication methods, and how to choose the right one for your next project.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Hardware Cloth?
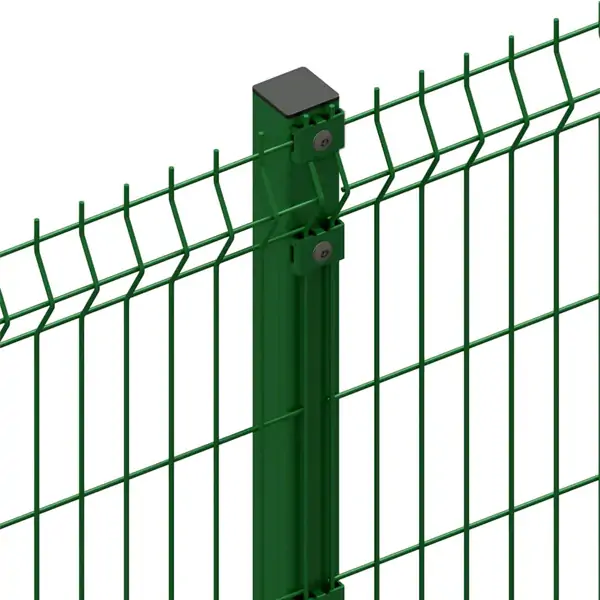
Hardware cloth is a type of wire mesh characterized by its grid-like pattern of square or rectangular openings. Unlike softer mesh materials, hardware cloth is made from rigid wire—typically steel—that is welded or woven together. It is commonly used as a protective screen or barrier in construction, agriculture, and home improvement applications.
Key features include:
-
Made from steel wire
-
Square or rectangular mesh openings
-
Available in different gauges and coating types
-
Can be cut, shaped, and installed easily
Types of Hardware Cloth
Understanding the different types of hardware cloth will help you make the right decision for your needs. There are three main ways to classify hardware cloth: by material, by construction method, and by mesh size.
1. By Material
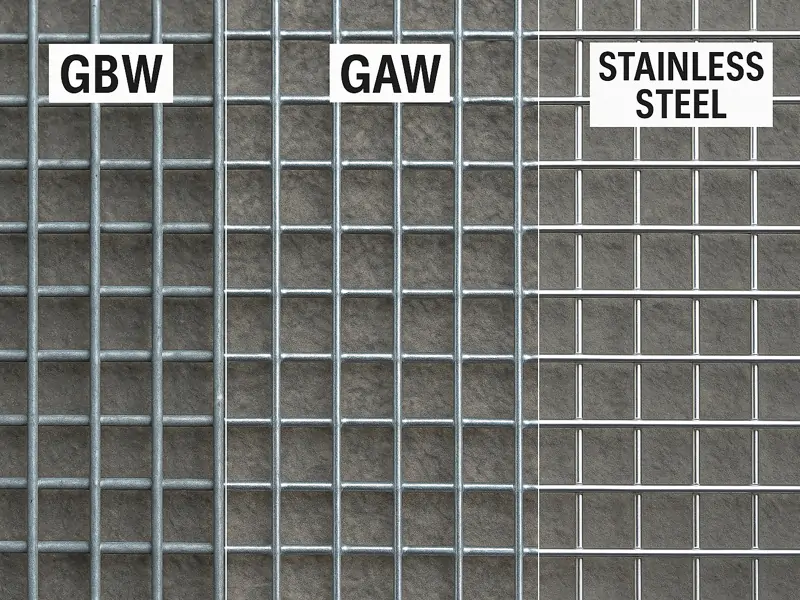
Galvanized Before Weaving (GBW)
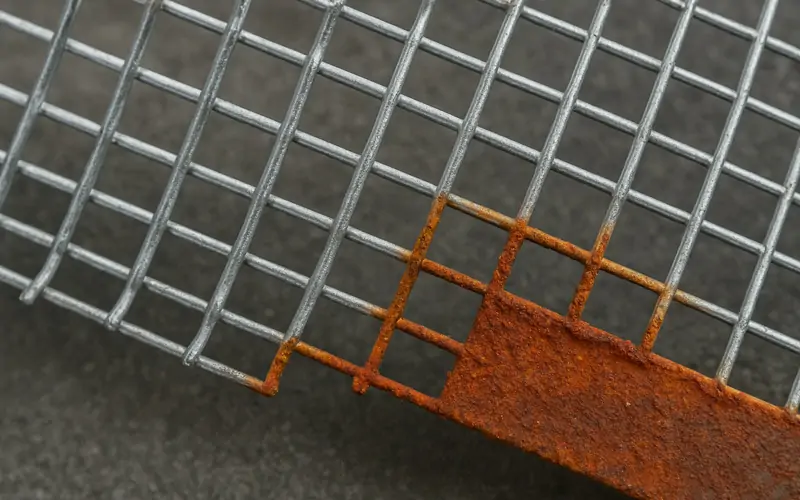
This type of hardware cloth is galvanized first, then woven or welded. It’s cheaper but more prone to rust at weld points.
Galvanized After Weaving (GAW)
This version is woven or welded first, then dipped in molten zinc. It offers superior corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel
Extremely durable and rust-resistant. Ideal for marine environments or food-processing areas.
PVC-Coated
A layer of plastic coating is applied over galvanized wire. This adds a weatherproof and attractive finish.
2. By Construction Method
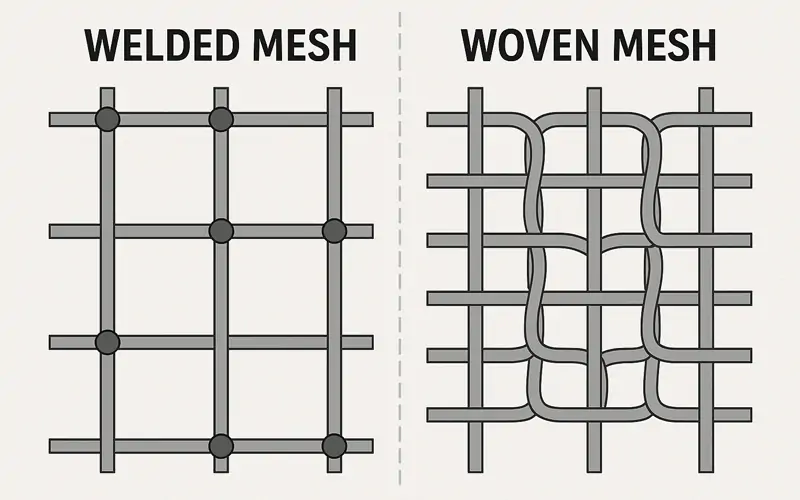
Welded Hardware Cloth
Individual wires are welded together at the intersections. This creates a strong, rigid sheet that holds its shape well.
Woven Hardware Cloth
Wires are woven over and under each other, similar to fabric. This is more flexible than welded cloth but slightly less sturdy.
3. By Mesh Size and Wire Gauge
Mesh size refers to the width of the opening between the wires, while wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire itself.
| Mesh Size | Common Applications | Wire Gauge |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | Insect screens, vents | 27–23 |
| 1/4″ | Rodent control, small cages | 23–19 |
| 1/2″ | Garden fencing, coops | 19–16 |
| 1″ | General fencing, enclosures | 16–14 |
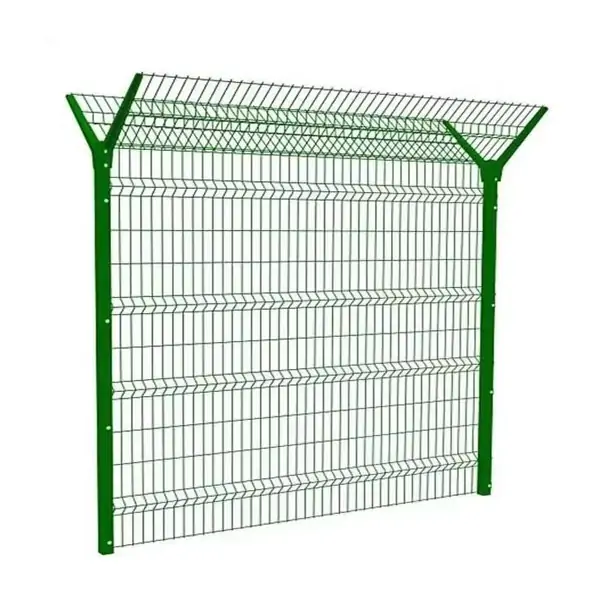
Common Applications of Hardware Cloth
1. Home & Garden
Homeowners commonly use hardware cloth for:
-
Pest-proofing crawl spaces or attics
-
Gutter guards
-
Compost bins
-
Tree trunk protection
-
Raised garden beds
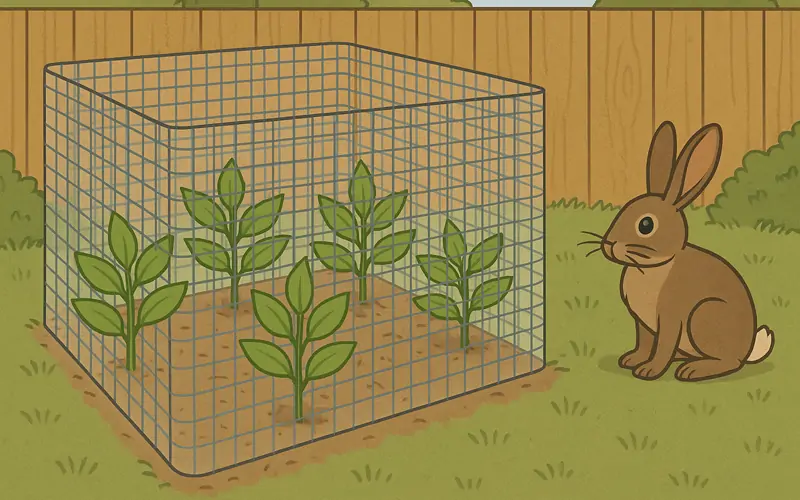
2. Agricultural Uses
In farming and livestock settings, hardware cloth serves as:
-
Chicken coop wire
-
Rabbit cage fencing
-
Crop protection against birds and rodents
-
Livestock feeder guards
Its rigidity and resistance to chewing make it far more effective than chicken wire in most agricultural tasks.
3. Industrial & Construction
Contractors and engineers use hardware cloth for:
-
Concrete reinforcement (as lath or mesh)
-
Ventilation screens in HVAC systems
-
Machine safety guards
-
Scaffold protection and debris control
4. DIY & Craft Projects
Creative users love hardware cloth for:
-
Custom storage racks
-
Art installations and sculptures
-
Lampshades and home decor
-
Rustic cabinet doors
Fabrication and Manufacturing Process
The way hardware cloth is made affects its performance and longevity. Here’s how it’s typically manufactured:
1. Material Selection
Most hardware cloth starts with carbon steel wire. For corrosion resistance, stainless steel or pre-galvanized wire is also used.
2. Weaving or Welding
-
Welded mesh: Each intersection is welded by machine.
-
Woven mesh: Wires are crimped and interwoven in a loom-like fashion.
3. Coating or Finishing
-
Galvanized Before Weaving (GBW)
-
Galvanized After Weaving (GAW)
-
PVC Coating or Powder Coating for additional weather resistance
4. Cutting and Packaging
Hardware cloth is usually cut into rolls or sheets and packed with protective wrapping for shipping.
How to Choose the Right Hardware Cloth
Choosing the best hardware cloth depends on your specific application. Ask yourself:
-
Where will it be used?
Outdoor settings require rust-resistant options like GAW or PVC-coated. -
What are you trying to block or contain?
Rodents? Go with 1/4″ or smaller. Chickens? 1/2″ works fine. -
Do you need flexibility or rigidity?
Choose woven for flexibility, welded for stiffness. -
How long should it last?
Stainless steel lasts the longest but comes at a higher price.
Maintenance Tips
To extend the life of your hardware cloth:
-
Keep it clean: Brush off dirt and debris regularly
-
Avoid prolonged moisture exposure
-
Seal cut edges with galvanizing spray
-
Check for rust spots and repair promptly
Conclusion
Hardware cloth is a powerful yet simple material that serves countless purposes in homes, farms, and job sites. Understanding the types, materials, and applications can help you choose the right product for your specific needs—saving you time, money, and frustration.
Whether you’re reinforcing a concrete slab or building a backyard chicken coop, this all-in-one guide has given you the foundation to select, use, and maintain hardware cloth like a pro.