Understand the key differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel wire mesh, including composition, corrosion resistance, applications, and cost. This in-depth guide helps you choose the right mesh for your needs.
جدول المحتويات
تبديلIntroduction
Stainless steel wire mesh is an essential material widely used in industries ranging from construction and agriculture to filtration and architecture. When choosing stainless steel wire mesh, two grades frequently come into discussion: 304 and 316. Understanding the differences between these two alloys can help you select the right mesh for your project, ensuring durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide will explain the fundamentals of stainless steel alloys, compare 304 and 316 wire mesh in depth, explore their applications, and offer guidance on how to choose the best alloy for your needs.
Understanding Stainless Steel Alloys
What is Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is a versatile alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium, and varying amounts of other elements such as nickel and molybdenum. The chromium content, usually above 10.5%, creates a thin protective oxide layer on the surface, which prevents rust and corrosion, giving stainless steel its characteristic resistance.
Two of the most commonly used stainless steel alloys in wire mesh production are 304 and 316. Both belong to the austenitic stainless steel family, meaning they have a face-centered cubic crystal structure that provides excellent strength and ductility.
304 vs 316: The Role of Molybdenum and Carbon
The key difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel lies in their chemical composition. Both contain roughly 18% chromium and 8% nickel, but 316 includes an additional 2–3% molybdenum. This small addition significantly improves corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and other industrial chemicals.
Carbon content is typically low in both alloys, enhancing corrosion resistance further and reducing the risk of carbide precipitation during welding.
In-Depth Comparison: 304 vs. 316 Stainless Steel Mesh
Chemical Composition
-
304 Stainless Steel: Contains 18–20% chromium, 8–10.5% nickel, and very low carbon (usually <0.08%). It does not contain molybdenum.
-
316 Stainless Steel: Contains similar chromium and nickel but adds 2–3% molybdenum and sometimes slightly lower carbon content.
Molybdenum enhances the alloy’s resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion caused by chlorides and saltwater.
Corrosion Resistance
304 stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance in most environments, including atmospheric conditions, fresh water, and many chemicals. However, it is vulnerable in chloride-rich environments such as coastal areas or chemical processing plants.
316 stainless steel is specifically designed to resist corrosion in harsh environments containing chlorides. It withstands saltwater exposure, acidic and alkaline solutions, making it ideal for marine, medical, and chemical industries.
Strength and Durability
Both 304 and 316 stainless steel mesh offer high tensile strength and durability. Their austenitic nature allows for good formability and weldability. However, due to molybdenum addition, 316 exhibits better resistance to cracking and longer lifespan in aggressive environments.
Cost Differences
316 stainless steel is more expensive than 304 due to the additional molybdenum and more complex manufacturing process. If your application does not involve corrosive elements like salt or chemicals, 304 provides excellent value for general use.
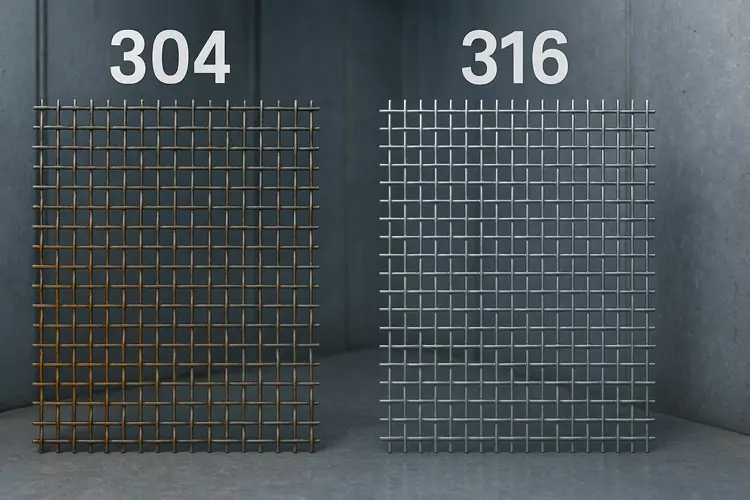
Visual Identification
Physically distinguishing 304 from 316 stainless steel wire mesh by appearance alone is nearly impossible as both have a similar shiny, silvery finish. Identification usually requires mill test certificates or chemical analysis.
Applications and Use Cases
304 Stainless Steel Mesh Applications
-
Air and liquid filtration
-
Industrial sieving and screening
-
Architectural features and fencing
-
Food processing equipment (non-corrosive environments)
-
Animal enclosures and cages
316 Stainless Steel Mesh Applications
-
Marine and coastal construction
-
Chemical processing plants
-
Pharmaceutical and medical devices
-
Saltwater aquaculture
-
Food processing in highly corrosive environments
Which Alloy Should You Choose?
Choosing between 304 and 316 stainless steel mesh depends on your project’s specific needs. Consider the environment, exposure to chemicals or salt, budget, and required lifespan.
| Feature | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (general use) | Excellent (harsh/corrosive environments) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| المتانة | High | Higher |
| Suitable Environments | Indoor, mild climates | Marine, chemical, acidic, coastal |
If your project is in a non-corrosive environment and cost-sensitive, 304 is suitable. For marine or chemical exposure, 316 is the best choice despite the higher cost.
Where to Source Quality Stainless Steel Mesh
When buying stainless steel wire mesh, verify:
-
Authentic mill certificates proving the grade
-
Trusted suppliers with positive reviews
-
Material testing reports
-
Availability of customization (mesh size, wire diameter, finish)
-
Competitive pricing balanced with quality assurance
Both online and offline suppliers have pros and cons. Online suppliers offer convenience and wide selections, while local suppliers can provide immediate support and faster delivery.
الخاتمة
304 and 316 stainless steel wire mesh each have unique strengths tailored to different applications. Understanding their composition, corrosion resistance, and cost will help you make an informed choice. Selecting the right alloy ensures your mesh performs reliably in its intended environment and offers lasting value.
For general purposes, 304 is cost-effective and reliable. For harsh, corrosive environments, especially marine and chemical industries, 316 stainless steel mesh is the superior option. Always purchase from reputable suppliers to guarantee authenticity and quality.